What are varicose veins?
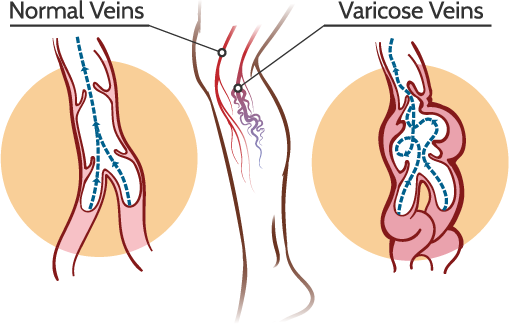
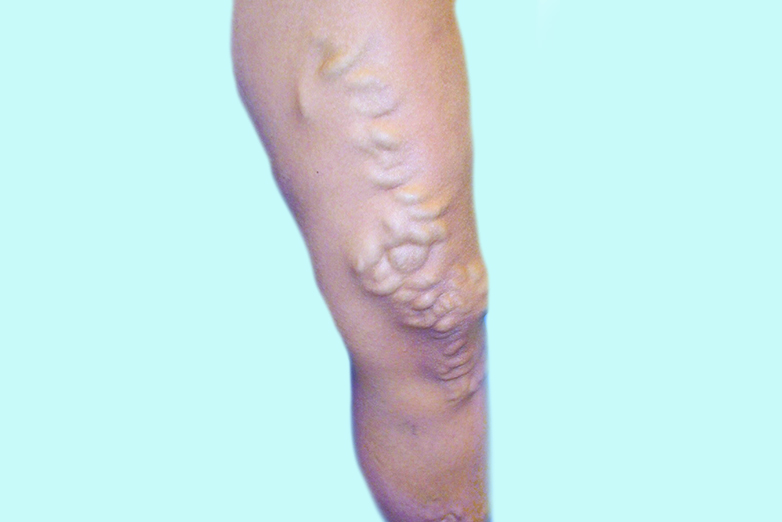
Varicose veins are enlarged, swollen, and often twisted veins that typically appear blue or dark purple in color. They usually develop in the legs and can be seen bulging under the surface of the skin. Varicose veins occur when the valves within the veins weaken or fail to function properly. Veins have one-way valves that help blood flow upwards towards the heart. When these valves weaken or become damaged, blood can flow backward and pool in the veins, causing them to swell and enlarge.
Risk Factors:
Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins:
- Heredity: Genetics play a significant role in determining whether someone is prone to developing varicose veins. If close family members have them, there's a higher chance of developing them as well.
- Age: As people get older, the valves in their veins may weaken, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins than men, partly due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, premenstruation, or menopause.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy increases the volume of blood in the body and puts extra pressure on the veins. Varicose veins that develop during pregnancy often improve within a few months after delivery.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts added pressure on veins, which can contribute to the development of varicose veins.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Jobs or lifestyles that involve prolonged periods of standing or sitting can hinder blood flow and contribute to the formation of varicose veins.
Symptoms:
While many patients have minimal or no symptoms, some symptoms associated with varicose veins vary but commonly include:
- Aching or discomfort in the affected area, especially after prolonged standing or sitting.
- Swelling, usually mild, around the ankles and calves.
- Heaviness or a feeling of fullness in the legs.
- Itching over the veins.
- Skin changes, such as discoloration or darkening around the veins.
- Complications from varicose veins are uncommon but can include skin ulcers, bleeding from the veins, and superficial thrombophlebitis (inflammation and clotting in a vein just below the skin).
Treatment:
There are several treatments available for
varicose veins, ranging from conservative
measures to more invasive procedures depending
on the severity and symptoms of the condition.
Treatments aim to alleviate symptoms, improve
appearance, and prevent complications.
Lifestyle Changes
Regular physical activity can improve
circulation and strengthen the muscles in
the legs.
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces
pressure on veins.
A high-fiber diet can prevent constipation,
which may exacerbate varicose veins.
Elevating the legs periodically can help
reduce swelling and improve circulation.
Compression Stockings
Graduated compression stockings apply
more pressure at the ankle and gradually
lessens toward the knee or thigh.
These stockings can alleviate symptoms
and prevent the progression of varicose
veins by improving blood flow.
Sclerotherapy
A solution is injected directly into the
affected veins, causing them to collapse
and fade.
Multiple sessions may be required, and
results typically appear over weeks to
months.
Laser Treatments
Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT). A
laser fiber is inserted into the vein,
delivering energy that heats and closes
the vein.
Surface Laser Treatments. Non-invasive
lasers can treat smaller spider veins by
causing them to fade without injections.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
A catheter is inserted into the vein,
delivering radiofrequency energy that
heats the vein walls and causes them to
close.
Minimally invasive with a quick recovery
time.
Vein Stripping
Involves removing larger varicose veins
through small incisions.
Typically reserved for more severe cases
and may require general anesthesia.
Recovery time with this procedure is
typically 2-4 weeks.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy
Small incisions are made in the skin to
remove varicose veins. It is performed
under local anesthesia.
Quick recovery with minimal scarring.
Vein Ligation
Involves tying off a vein to prevent blood
from pooling. This can be done alongside
stripping or as a standalone treatment.
Often performed when other treatments
are not suitable.
Endovenous Chemical Ablation
A chemical solution is injected to cause
irritation and closure of the vein.
Similar to sclerotherapy this method is
used for larger veins and can provide a
long-term solution.
Post-Treatment Care
Most of these treatments require minimal
attention after they are preformed. In most
cases, regular daily activity can be
resumed the same day, while strenuous
activity is to be avoided for up to 14 days.
Alway be sure to discuss any potential
recovery issues or concerns with the
doctor before the procedure, regardless of
which procedure you decide on.
Regular check-ups are essential to
monitor for recurrence.
Use of Compression Stockings is required
after these procedures to enhance
recovery and prevent new varicose veins
from forming.
A 1-month post procedure ultrasound and
in-office followup are scheduled for all
procedures.
Of the many types of procedures, the Laser Vein
Clinic focuses on EVLT, Venaseal™ Glue and
Foam Sclerotherapy for the treatment and
removal of varicose veins.
Book an appointment today and begin the
process to give your varicose veins the treatment
they deserve!
Before and after the EVLT procedure.
Treatment:
Those with minimal symptoms may be able to manage with compression stockings and
lifestyle changes alone. For those experiencing symptoms, there are several treatments
available for varicose veins, ranging from conservative measures to more invasive procedures
depending on the severity and symptoms of the condition. Treatments aim to alleviate
symptoms, improve appearance, and prevent complications.
Lifestyle Changes
Regular physical activity can improve circulation and strengthen the muscles in the legs.
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on veins.
A high-fiber diet can prevent constipation, which may exacerbate varicose veins.
Elevating the legs periodically can help reduce swelling and improve circulation.
Most patients with varicose veins can be managed conservatively.
Compression Stockings
Graduated compression stockings apply more pressure at the ankle and gradually
lessens toward the knee or thigh.
These stockings can alleviate symptoms and prevent the progression of varicose veins
by improving blood flow.
When used diligently, compression stockings can be an alternative to surgery or laser
ablations.
Sclerotherapy
A solution is injected directly into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and fade.
Multiple sessions may be required, and results typically appear over weeks to months.
Laser Treatments
Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT). A laser fiber is inserted into the vein, delivering
energy that heats and closes the vein.
Surface Laser Treatments. Non-invasive lasers can treat smaller spider veins by causing
them to fade without injections.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
A catheter is inserted into the vein, delivering radiofrequency energy that heats the vein
walls and causes them to close.
Minimally invasive with a quick recovery time.
Vein Stripping/Ligation
Involves removing larger varicose veins through small incisions.
Typically reserved for more severe cases and may require general anesthetic and is
performed in the hospital.
Recovery time with this procedure is typically 2-4 weeks and carries the risk of wound
complications.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy
Small incisions are made in the skin to remove varicose veins. It is performed under local
anesthetic and often in the office setting.
Quick recovery with minimal scarring.
Endovenous Chemical Ablation
A chemical solution is injected to cause irritation and closure of the vein.
Similar to sclerotherapy this method is used for larger veins and can provide a long-term
solution.
This procedure is not offered in the Laser Vein Clinic.
Post-Treatment Care
Most of these treatments require minimal attention after they are preformed. In most
cases, regular daily activity can be resumed the same day, while strenuous activity is to
be avoided for up to 14 days.
Alway be sure to discuss any potential recovery issues or concerns with the doctor
before the procedure, regardless of which procedure you decide on.
Regular check-ups are essential to monitor for recurrence.
Use of Compression Stockings is required after these procedures to enhance recovery.
A 1-month post procedure ultrasound and in-office followup are scheduled for all
procedures.
Of the many types of procedures, the Laser Vein Clinic focuses on EVLT, Venaseal™ Glue and
Foam Sclerotherapy for the treatment of varicose veins.
Book an appointment today and begin the process to give your varicose veins the treatment
they deserve!